Overview
Ending hunger and enabling safe, affordable, healthy diets for the world’s most vulnerable people
Food security and nutrition are key to human well-being. Far too many people around the world are affected by malnutrition ranging from undernutrition to problems of overweight, obesity, and diet-related noncommunicable diseases. Achieving sustainable healthy diets….
IFPRI research addresses food insecurity from multiple angles, including providing foresight and real-time monitoring on market supply and trade of major crops; policies and investments to improve availability of food through better infrastructure, logistics, and markets; the role of social protection programs, including cash transfers, in improving food security and diets; and Work on gender and equity explores how access to and decision-making around food production, sale, and consumption affect food security and nutrition, and the policies and educational programs that can improve access for women, children, and adolescent girls.
To understand the intrinsic links between food systems, nutrition, and health, IFPRI addresses a range of issues antimicrobial resistance, nutrition-associated noncommunicable diseases, food safety, intimate partner violence, malnutrition, maternal and child health, social protection, and nutrition programs linked with agriculture and education programs to social protection. Improving nutrition requires contributions not only from the health sector but also from sectors as diverse as agriculture, social protection, gender, and education, which together can address the underlying causes of malnutrition. IFPRI’s nutrition research aims to generate rigorous evidence on what works—and what does not—to prevent malnutrition in low- and middle-income countries. IFPRI’s nutrition research expertise covers nutrition and dietary assessment; infant and young child nutrition; adolescent nutrition; maternal nutrition; and school-based and other multisectoral nutrition programs. IFPRI’s work on biofortification, which …., has increased access to essential nutrients for 100 million people, through development and dissemination of biofortified crops, including….
CGIAR Research Initiatives
- FRESH
- SHiFT
- National Policies and Strategies
- Resilient Cities
Learn more about IFPRI’s work on nutrition, health, and food security
What’s New
-

Trust the messenger? The role of AI transparency in policy research communication
Testing reader responses to chatbot- vs. human-written blog posts.
-
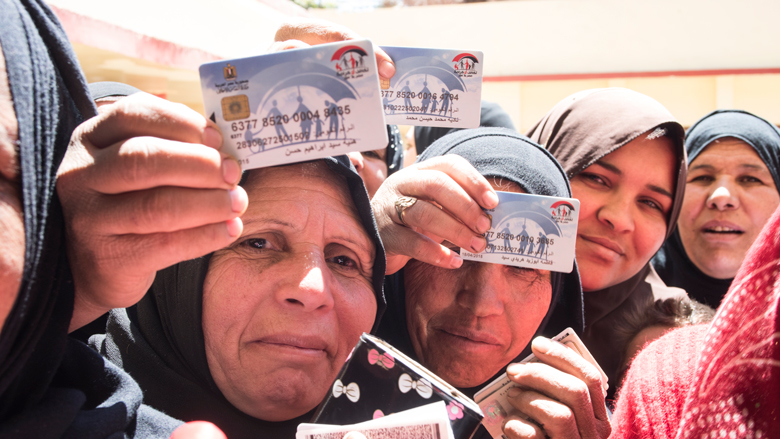

Takaful program: Giving Egypt’s poor a hand up, not just a handout
Assessing impacts of cash transfers.
-
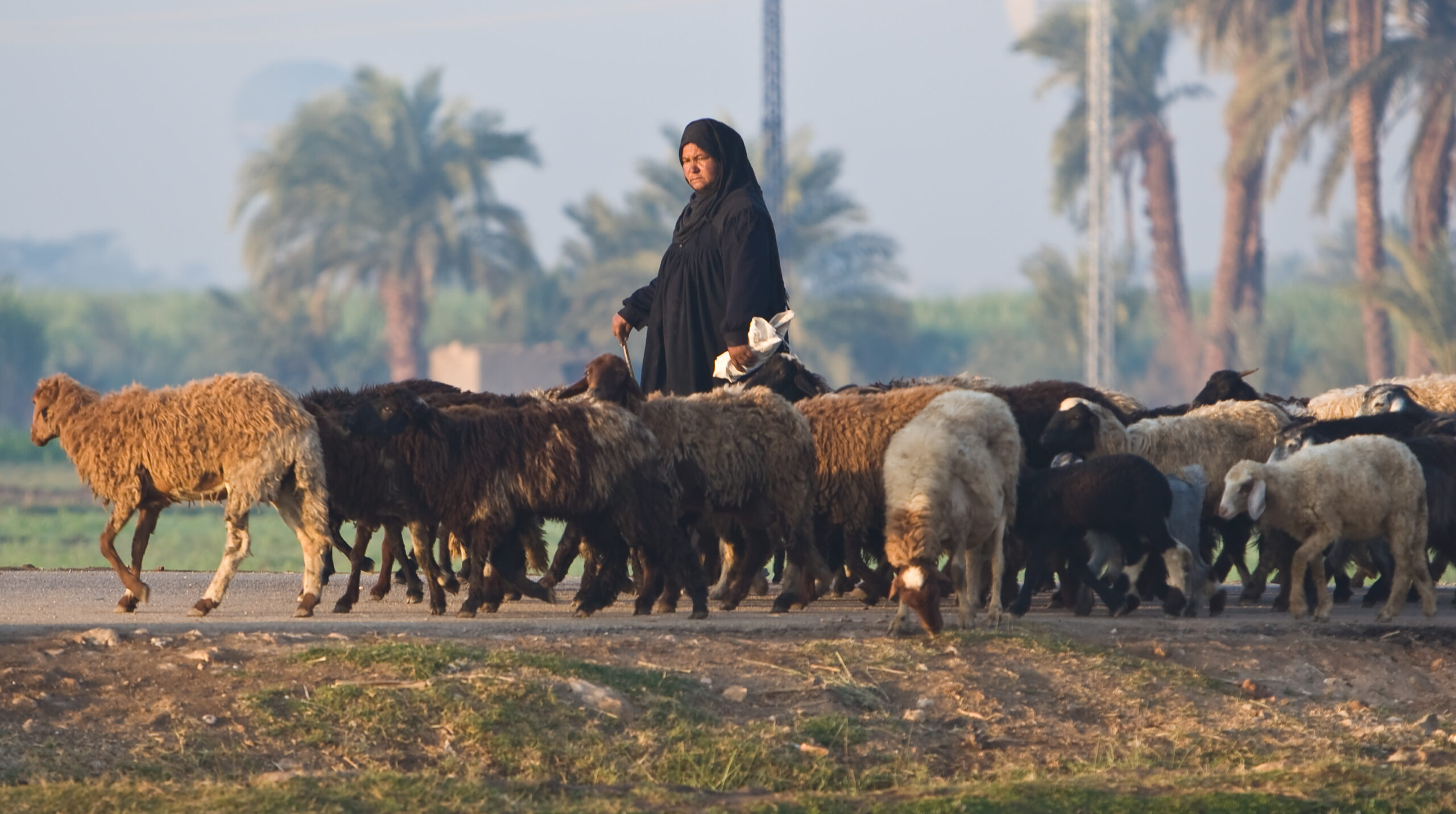

Egypt’s experience bridging cash transfers and an economic inclusion program for sustainable social protection
A path for moving out of poverty.
Nutrition, health, and food security by the numbers
Food security and nutrition are key to human well-being. Far too many people around the world are affected by malnutrition ranging from undernutrition to problems of overweight, obesity, and diet-related noncommunicable diseases.
US$1B
estimated economic returns on just a few of IFPRI’s research efforts
46
gold standard impact assessment reports commissioned
27
years of measuring institutional impact
412
million/people indirectly benefitting from IFPRI
Explore our research
Journal Article
Adapting the women’s empowerment in nutrition index: Lessons from Kenya
Journal Article
Adapting the Women’s empowerment in nutrition index: Lessons from Kenya
Journal Article
Information framing effects on diet choices among Chinese urban residents
Events
-

Food Systems for Healthy Diets and Nutrition: The MENA launch of IFPRI’s 2024 Global Food Policy Report
Unhealthy diets are a major driver of all forms of malnutrition, including undernutrition, micronutrient deficiencies, and overweight and obesity. Despite increasing global efforts to address malnutrition, as many as 3 billion people globally cannot afford healthy diets. The need to transform our food systems to ensure sustainable healthy diets for everyone is more urgent than…
-

Food Systems Transformation in Kenya: Lessons from the Past and Policy Options for the Future
Hybrid Event: January 8, 2023 at 8:30am-9:45am EST/ 4:30pm-5:45pm EAT. During this hybrid book launch, speakers from academia, Kenyan research institutes, policy institutions, and CGIAR will discuss the new book Food System Transformation in Kenya: Lessons from the Past and Policy Options for the Future. A light reception will follow the presentations.
-
The E-FooD Dataset and Food Security Simulators for Kenya and Nigeria: Innovative Tools to Support National Policies and Strategies
Virtual Event: December 7, 2023 – 8:00 AM- 9:00 AM EST. This webinar, organized by the CGIAR Initiative on National Policies and Strategies (NPS), introduces the E-FooD dataset and FSS for Kenya and Nigeria, showcases their applications, and discusses the role that such tools can play in policymaking.




