Public expenditure is a powerful instrument for governments to use in achieving sustainable growth, poverty reduction, and transformation. Understanding the linkages between different types of public expenditure and development can help governments to better allocate their resources in a manner consistent with their policy objectives and citizens’ needs and priorities. Development practitioners, donors, and the general public have increasingly requested expenditure accountability and transparency in the use of public resources. Transparency in public spending allows governments to better track, monitor, and evaluate the impacts of investment decisions and to invest in the provision of public goods and services that benefit the rural poor (such as agricultural research and extension, health, education, and social protection) and provide a conducive environment for private-sector investments.
Against this background, the International Food Policy Research Institute (IFPRI) launched and made publicly available the Statistics on Public Expenditures for Economic Development (SPEED) database in 2010. The database aims to provide policymakers, researchers, and the broader development community with the most comprehensive public expenditure information. SPEED 2019 is the third major update of the database since 2010 (the first and second major updates were made available in 2013 and 2015 respectively). This third update includes:
- an expanded time coverage (1980 to 2017).
- an expanded country coverage (164 countries);
- additional currencies (LCU, Current US Dollars, Constant 2010 US Dollars);
- inclusion of World Bank regions
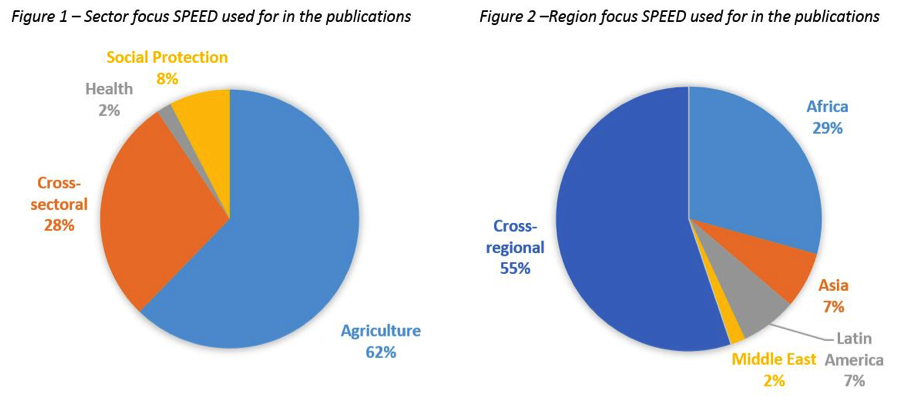
The SPEED database tracks public expenditures for development, including for agriculture, to allow policymakers and analysts to examine policy priorities, track development goals, and explore the cost-effectiveness of public spending either within a country or across countries within a region or at a similar level of development over a long timeframe. The 2019 SPEED update includes data for 166 countries in eleven public expenditure sectors: agriculture, communication, education, defense, health, mining, social protection, fuel and energy, transport, transport and communication (as a group) and other. User-friendly tools on the SPEED website enable the generation of accessible charts and geographic expenditure maps, in addition to direct data downloads.
For more information, please contact ifpri-speed@cgiar.org