Overview
IFPRI’s seven research units focus on research and innovation to deliver integrated policies, investments, governance processes, and capacity building in support of sustainable and equitable food systems transformation to deliver improved livelihoods and healthy diets.
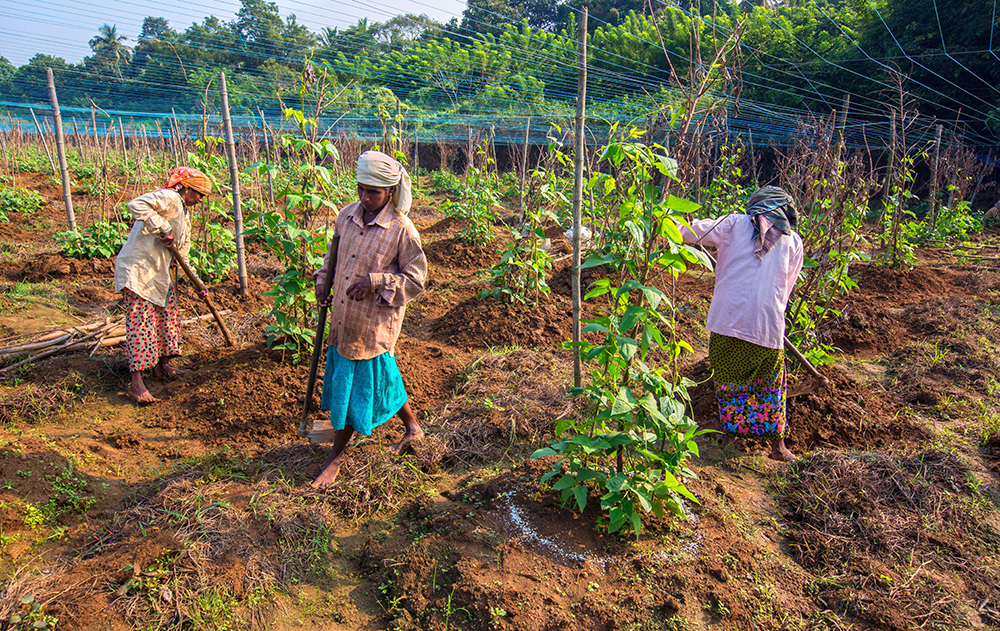

Development Strategies and Governance
Agrifood systems play a critical role in economic development, poverty reduction, and nutrition improvement in low- and middle-income countries. Yet these systems face challenges from conflict, weather-related shocks, and political volatility that affect the prospects for equitable and sustainable growth. At the same time, rapid urbanization is reshaping patterns of food insecurity and elevating the importance of strong rural-urban linkages and decent off-farm jobs.
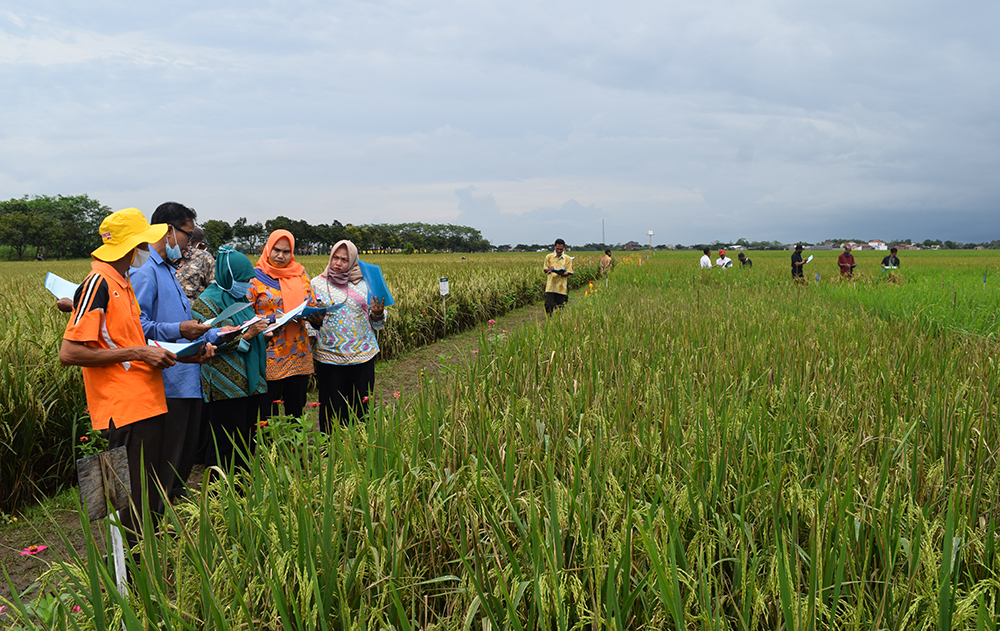

Foresight and Policy Modeling
Agrifood systems today are increasingly interconnected, but their future is less certain than ever before. Decision-makers — both public and private — need advance information to understand the growing complexity of these systems, navigate climate uncertainty and frequent crises, and manage trade-offs between competing interests and development goals.
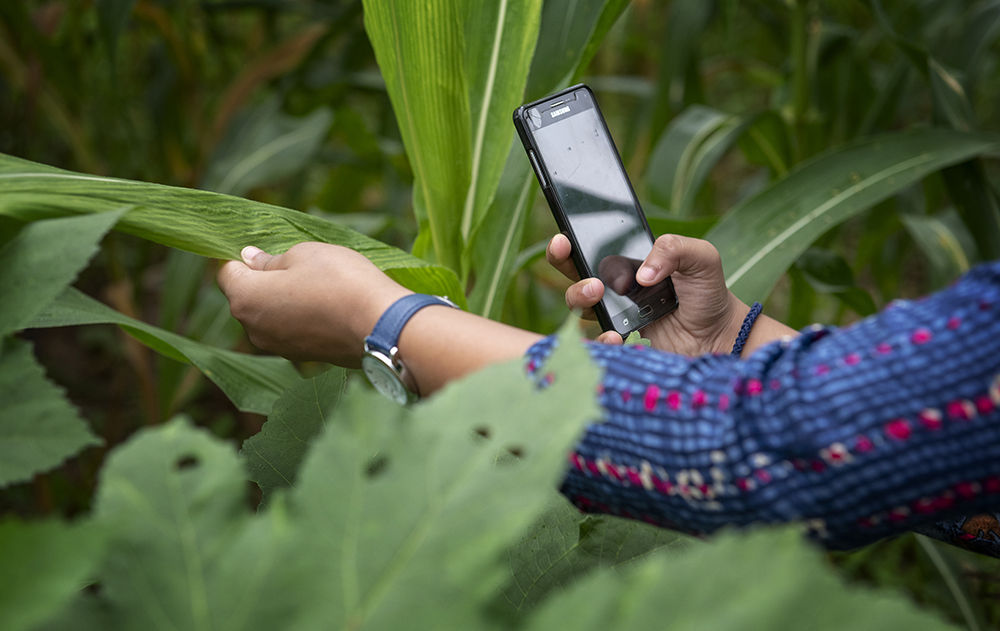

Innovation Policy and Scaling
Effective innovation systems at the national, regional, and global levels are critical to improving agricultural productivity, nutrition, equity, inclusion, and climate resilience. The Innovation Policy and Scaling Unit provides data-driven, evidence-based solutions to accelerate innovation at scale and advance inclusive and sustainable food systems transformation.
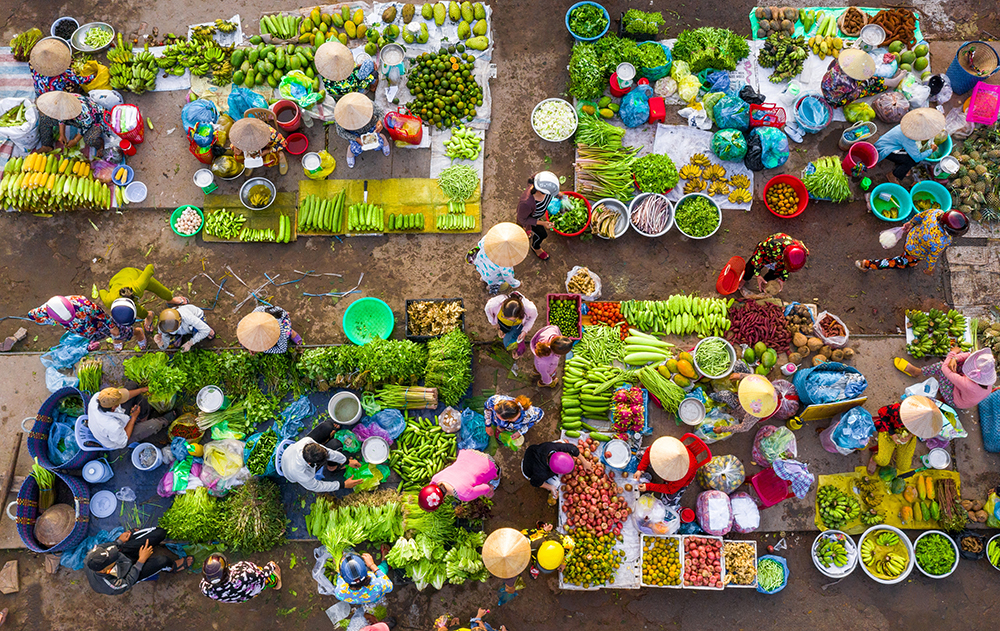

Markets, Trade, and Institutions
Drastic changes in the functioning of food markets are needed to achieve food security and adequate nutrition for all people, as well as contributing to poverty reduction and environmental sustainability.
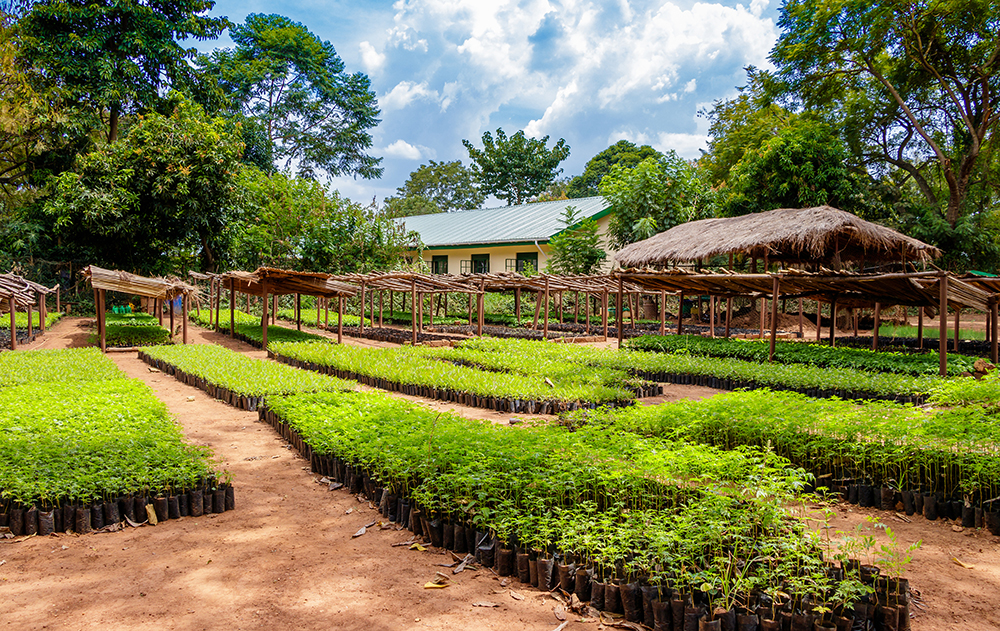

Natural Resources and Resilience
Climate change, resource degradation, and biodiversity loss increasingly threaten human well-being, food production, and nutrition. The Natural Resources and Resilience Unit works with partners to advance food security and nutrition while promoting sustainable resource use and more equitable outcomes for disadvantaged groups.
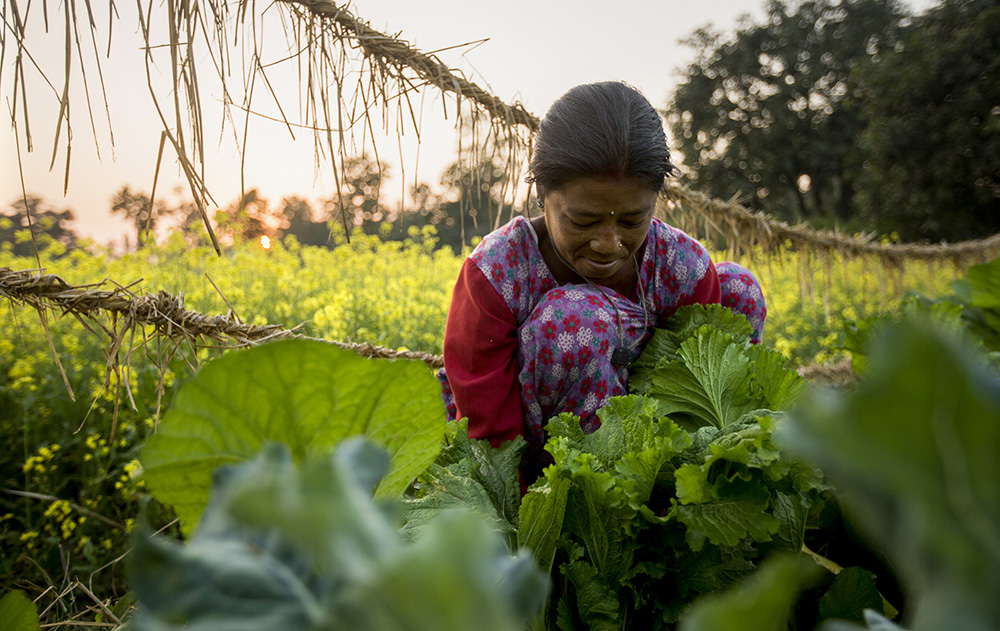

Nutrition, Diets, and Health
Poor diets are a primary cause of malnutrition and the leading cause of disease worldwide. Improving diets and addressing nutrition and health issues can improve people’s quality of life, increase their productivity, and save an estimated one in five lives annually.
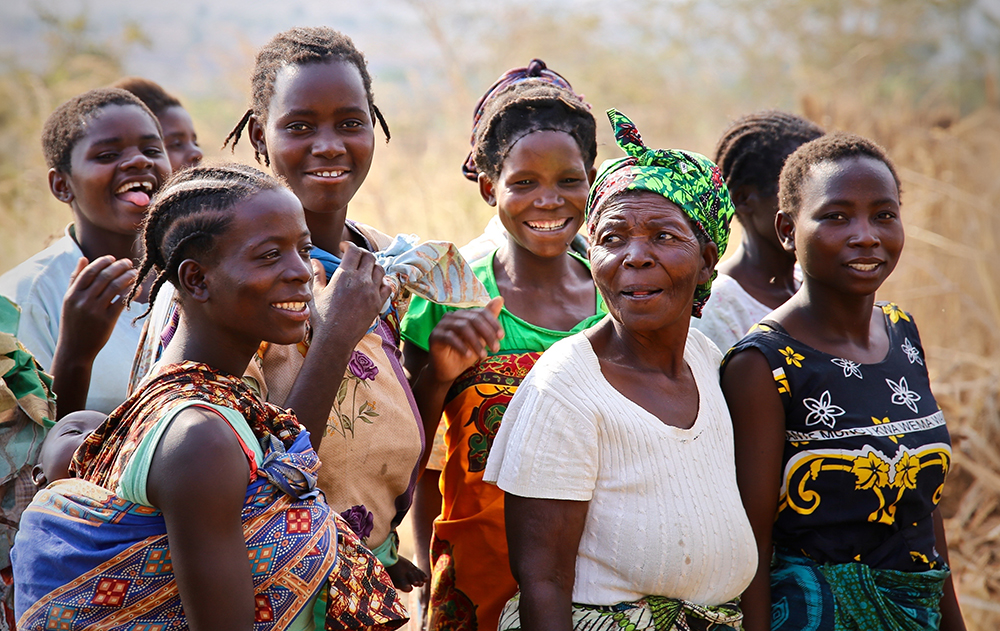

Poverty, Gender, and Inclusion
Improving access to resources and increasing participation and empowerment within agrifood systems is essential for improving well-being and livelihoods as well as increasing resilience of poor populations, particularly women and other vulnerable groups.