Workfare or public works employment programs have long been prominent in many developing countries. These programs can be a simple and direct strategy to reduce poverty among the poorest households, similar to cash transfers, but the additional requirement for employment can have several positive effects. First, the work requirement may effectively screen out those who have other, higher-return opportunities and thus improve targeting to the poor (Murgai et al. 2016). Second, employment can offer the opportunity for participants to build skills and gain experience and thus positively affect longer-term employment outcomes. Third, public workers can be engaged to construct or maintain local infrastructure, or assets that may have positive externalities (Gehrke et al. 2018).
In practice, however, direct evidence for these second and third channels is relatively weak. Many workfare programs require primarily low-skilled manual labor that is unlikely to result in any skills transfer, and may not have high returns in terms of asset creation (Murgai et al. 2016). Recent reviews of primarily quasi-experimental evidence have suggested that public works programs generally do not seem to boost employability or enhance skills (Gehrke et al. 2018).
Experimental design: Isolating the effect of public works employment
In a recently published article, we utilize a randomized controlled trial in Tunisia to evaluate the short- and long-term effects of the Community Works and Local Participation (CWLP) pilot, a public works program that provided short-term paid employment to the long-term unemployed (individuals reporting unemployment for at least a year) for three months (Leight and Mvukiyehe 2023). The evaluation employs a novel design in order to estimate treatment effects along multiple dimensions.
First, a community-level randomization assigned 80 rural villages to either treatment or control status. Second, local leaders identified eligible individuals in each community, and in treatment communities, a random subset of these eligible individuals were offered employment. The analysis thus allows us to compare three samples of interest: The eligible and treated individuals in treatment communities; the eligible and untreated individuals in treatment communities; and the eligible and untreated individuals in control communities. Figure 1 summarizes the experimental design.
Figure 1
The intervention and associated public works activities were rolled out between April and September 2015. During this period, individuals who were offered and took up employment earned around $180 per month or $550 total. This total amount is approximately equal to two months of consumption expenditure in the control arm. These public works activities included (but were not limited to): cleaning and rehabilitation of public parks or spaces; cleaning and rehabilitation of cultural or leisure infrastructure and services (e.g. maisons de jeunes, sports centers, etc.); rehabilitation of small roads in rural and peri-urban areas; rehabilitation of small roads and spaces leading to cultural sites of importance for the community; rehabilitation of schools and health centers; conservation and reforestation activities; and urban beautification activities.
The first follow-up survey of the primary sample of 2,718 individuals was implemented approximately one year later between April 2016 and January 2017. This was followed by a second, long-term follow-up conducted between December 2020 and April 2021, approximately five and half years following program implementation. The measured outcomes, all pre-specified, include labor force participation by both the target beneficiary and other household members, economic welfare, investment in human capital, social and civic engagement, psychosocial well-being, and women’s empowerment.
The short and long term effects of the public works program
The primary findings based on the cross-village comparison of treated and untreated individuals suggest that the intervention had significant and large short-term effects on both primary economic outcomes and secondary psychosocial outcomes, as summarized in Figure 2 below. There are increases in indices of labor market participation, assets, consumption, and financial inclusion of between 0.1 and 0.2 standard deviations, as well as increases of comparable magnitude in civic engagement, psychosocial well-being, and women’s empowerment. There were no effects of the intervention on human capital investment, coping mechanisms conditional on shocks, and social cohesion.
Figure 2
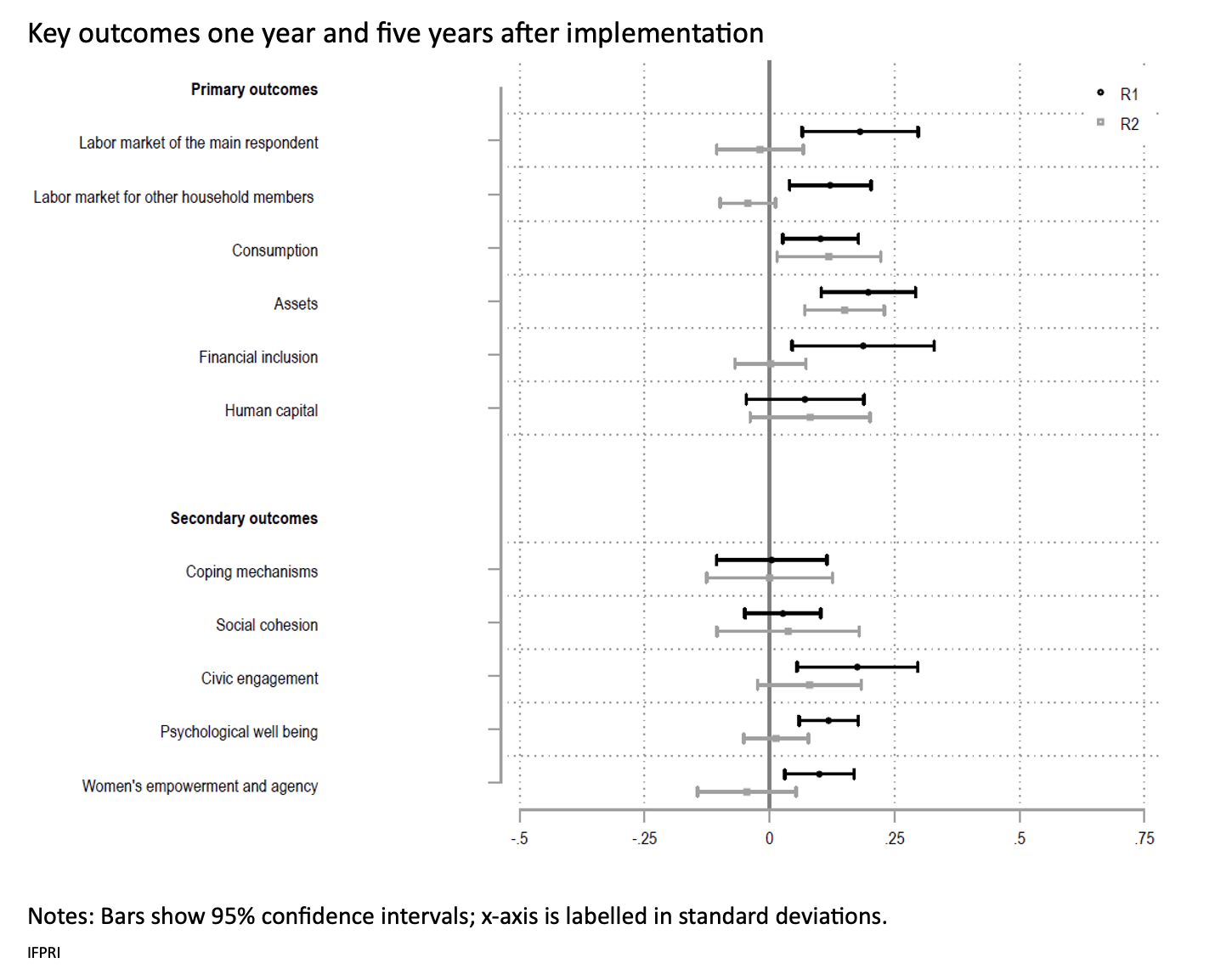
By the five-year follow-up, however, these effects have substantially attenuated toward zero. For economic outcomes, the positive effects on assets and consumption remain of comparable magnitude and are weakly statistically significant, but only the increase in assets remains significant when corrected for multiple hypothesis testing. The effects on other potential outcomes of interest are uniformly insignificant.
The cross-village comparison of untreated individuals in treatment and control communities—allowing for estimates of local spillover effects of the intervention—suggests a largely similar pattern. In the short run, there are positive spillover effects on the primary outcomes of similar magnitude (again between 0.1 and 0.2 standard deviations), other than for financial inclusion which is no longer significant. However, the effects on secondary outcomes are somewhat reduced. In the long run, none of the estimated spillover effects remain statistically significant.
Conclusion
Our findings suggest that engagement in short-term public works labor had no meaningful effects on shifting economic trajectories in the medium-term in this context. Poor households benefited from the transfer in boosting consumption and also saw other positive non-economic effects in the first year. Interestingly, these effects were large even for those who did not directly receive offers of employment, but who resided in the same community. These spillover suggest that public works programs could promote informal insurance or positive local demand effects. However, these effects do not persist. While we do not have direct data on actual infrastructure enhancements implemented as part of this program, the absence of any persistent spillover effects suggest that either those enhancements were limited and impermanent, or that they had limited benefits in terms of households’ welfare.
This new evidence adds to a growing evidence base, suggestive of some short-term but very limited persistent effects of short-term public works employment (Alik-Lagrange et al. 2017, Bertrand et al. 2017, Beegle et al. 2017, Brandily-Snyers et al. 2022). Nevertheless, these programs could still be a useful mechanism to provide a short-term buffer against adverse shocks or to smooth consumption. Moreover, given the absence of evidence that public works programs are effective in building skills or increasing employability, the relative advantage of these interventions vis-a-vis simpler social safety net programs remains an open question.
Jessica Leight is a Research Fellow with IFPRI’s Poverty, Gender, and Inclusion Unit; Eric Mvukiyehe is an Assistant Professor of Political Science at Duke University. This post first appeared on VoxDev. It is based on research that is not yet peer reviewed.
Referenced discussion paper:
Leight, Jessica; and Mvukiyehe, Eric. 2023. Short-term and long-term effects of cash for work: Evidence from a randomized controlled trial in Tunisia. IFPRI Discussion Paper 2184. Washington, DC: International Food Policy Research Institute (IFPRI). https://doi.org/10.2499/p15738coll2.136708
This work was supported by the World Bank Group and other donors through the Jobs Multi-Donors Trust Fund (Jobs MDTF), the Umbrella Facility for Gender Equality (UFGE), the MNA Gender Innovation Lab (MNAGIL), and the i2i Multi-Donors Trust Fund (i2i).







